Unipolar depression :
Evaluation of executive and attentional difficulties
and dynamical decision-making profiles with a new test
and using artificial intelligence
Raysséguier C., Vancappel A., Suarez S., El Hage W
Victory of the best poster at the JNPN 2023
Introduction:
Contexte :
- Executive functions are usually impacted in major unipolar depression.Executive dysfunction persistence is a relapse predictor.
- The current tools face challenges in specifying the affected component in depression and are not correlated with clinical observations, highlighting the need for more sensitive tools.
- MindPulse is a numerical evaluation test which enable the decomposition of executive and attentional functions,and the reaction to difficulty underlying fundamental decision-taking.
- An experimental version of MindPulse uses decision diffusion model (DDM) to catch the complex relationship between choices and reaction times by decomposing behavioral data in the cognitive processes responsible for decision-making
- A model of classification artificial intelligence (Not supervised AI) is tested to created Decision Evolution Profiles (DEP) by taking into account every factor including dynamical reaction throughout the test to compare DEP in typical and pathological samples.
Aims of the Study
- Show the the relationship between cognitive difficulties and Major Unipolar Depression symptomatology..
- To evaluate fundamental decision-taking ability in Major Unipolar Depression using MindPulse.
Population :
46 participants previously diagnosed with major unipolar depression (65% women). Mean age: 38,1 years old.
Cognitive evaluation :
Mindpulse battery (Decision-making) D2R (Sustained attention)
Stroop (Inhibition) Finger Tapping (Motor Speed)
Symptomatology evaluation:
MADRS (Depressive severity) S2T (Psychological difficulties)
T2S (Psychological abilities) ISI (Insomnia severity)
Results :
Correlation between cognitive evaluation and questionnaires
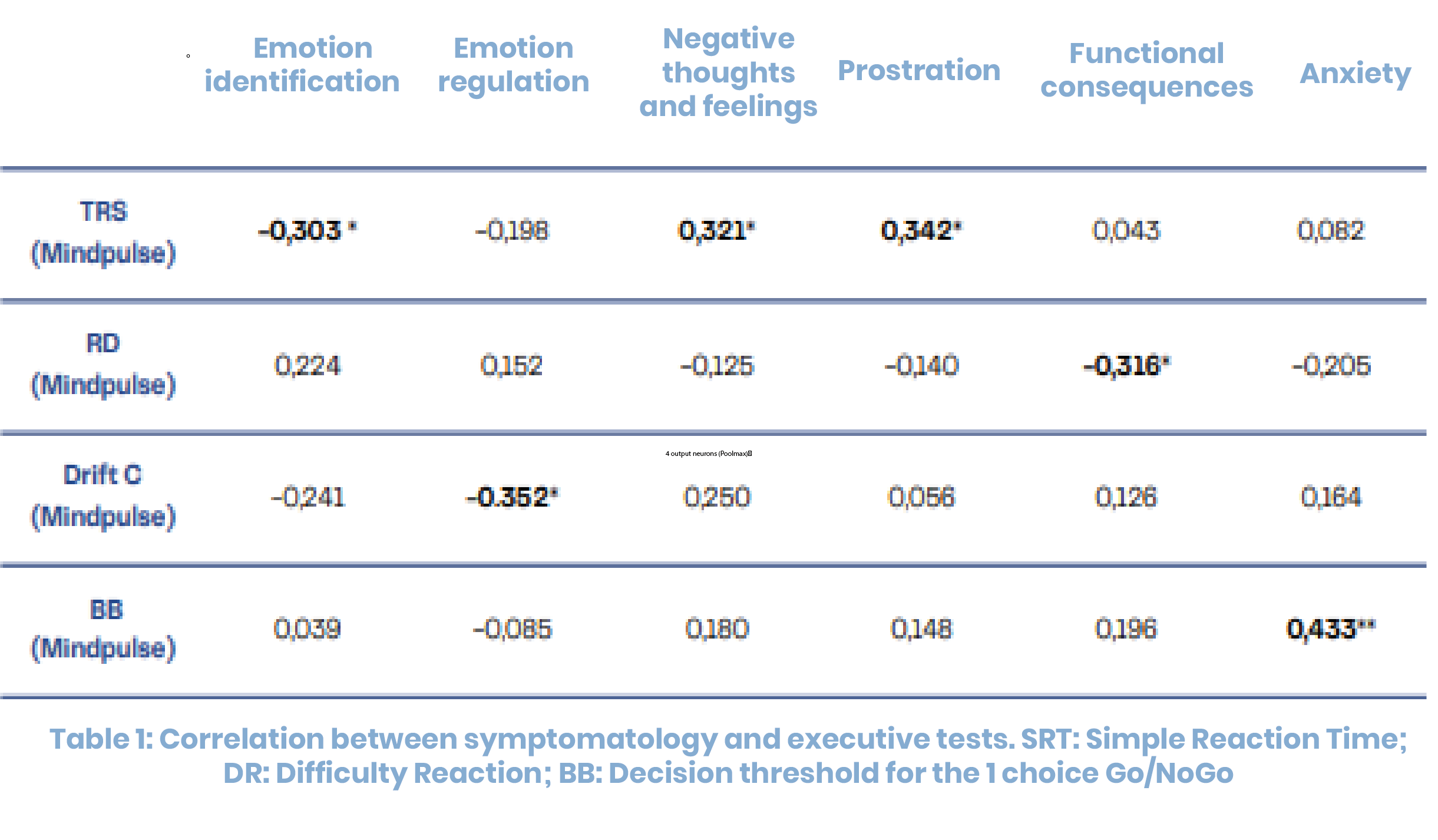
* Significant at p<.05 ** - Significant at p<.01
Stroop Indices for Interference Condition Time (IT) and Errors (EI) are NS.
D2-R indices for number of correct Responses (CCT) and Errors (%E) are NS.
MindPulse is the only test showing a correlation between depression symptomatology in this sample, meaning it’s the most precise test. Emotional Regulation appears to be linked to complex Go/NoGo Drift while DR is correlated to functional consequences.
Correlation between cognitive tests
- TRS – %E (r=,376, p=,05), C+
- Go No Go – CCT (r=-,497, p=,01), C-
- Go No Go – %E (r=,390, p=,01), C+
- Complex Go No Go – CCT (r=-,410, p=,01), C-
- RD – EI (r=- 427 , p=,01), C –
- Executive speed (Mindpulse) – CCT (r=-,394, p=,01), C+
Mindpulse indicators are correlated with Stroop and D2-r measures. Those correlations show that Stroop, D2-r and MindPulse are measuring the same parameters, but with more precision and sensibility for MindPulse..
Comparison between depressed participants and paired control group (age and sex) for MindPulse results :
An important slowing is found in depressed participant on the perceptivo-motor side (SRT t=2,72 p=.94%) and on the executive side (ES t=3.99 p=.03%). This double slowing comes with a lack of precision (increasement of the total errors t=2.97 p=.48%, mostly for inhibition and flexibility errors). The DDM Drift (difficulty perception) for each Go/NoGo subtasks (B and C) is significantly different for depressed participant and paired control group (Go/NoGo drift: t=-2,33 p=2.47%; Complex Go/NoGo drift: t=-2,17 p=3,55%). Drift shows the efficiency of decision processes, that is, the information accumulation rate towards the correct decision.
Depressed people show a different adjustment style in the complex subtasks. The increasement in the accumulation rate is consistent with existing literature.
Case Study: Major Depression :
19 y.o. female patient diagnosed with major depression, currently under medication (Venlafaxine, Xanax). Psychometric evaluation of her symptomatology shows a moderate anxietyand pathological scores in negative thoughts and feelings, prostration, planning, emotions identifications and problem solving.. In D2-r, she shows a processing style describes as neither focus nor attentive. Stroop test shows pathological scores on the Interference part. The MindPulse test highlights executive difficulties and a slowing in both perceptivo-motor and executive speed. The difficulty in adjustment to difficulty can be linked to her problem solving and planning issues. Those are helpful information for the practitioner to specify a treatment plan.
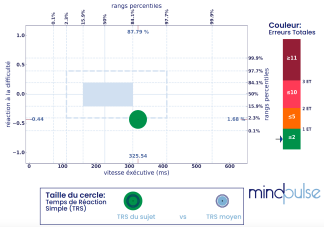
MindPulse Results:
- Very Slow Reaction Time (+4.16 ET)
- Moderate Slowing for Executive Speed (+1,16 ET)
- Normal Accuracy
- High overspeed difficulty reaction (-2,12 ET)
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence :
Decision Evolution profiles with Artificial Intelligence
- The addition of a classification Artificial Inteligency in Mindpulse enable to distinguished DEP to finely categorized cognitive profiles (DEP) by considering every factor without any information’s loss.
- DEP consider speed, accuracy, variability, and their evolutions during the test for each participant, including the changes occurring after and error.
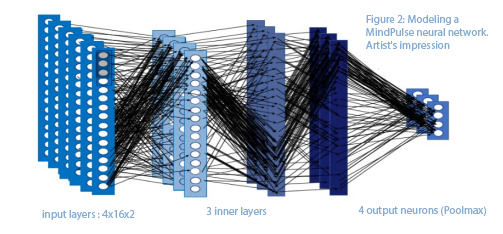
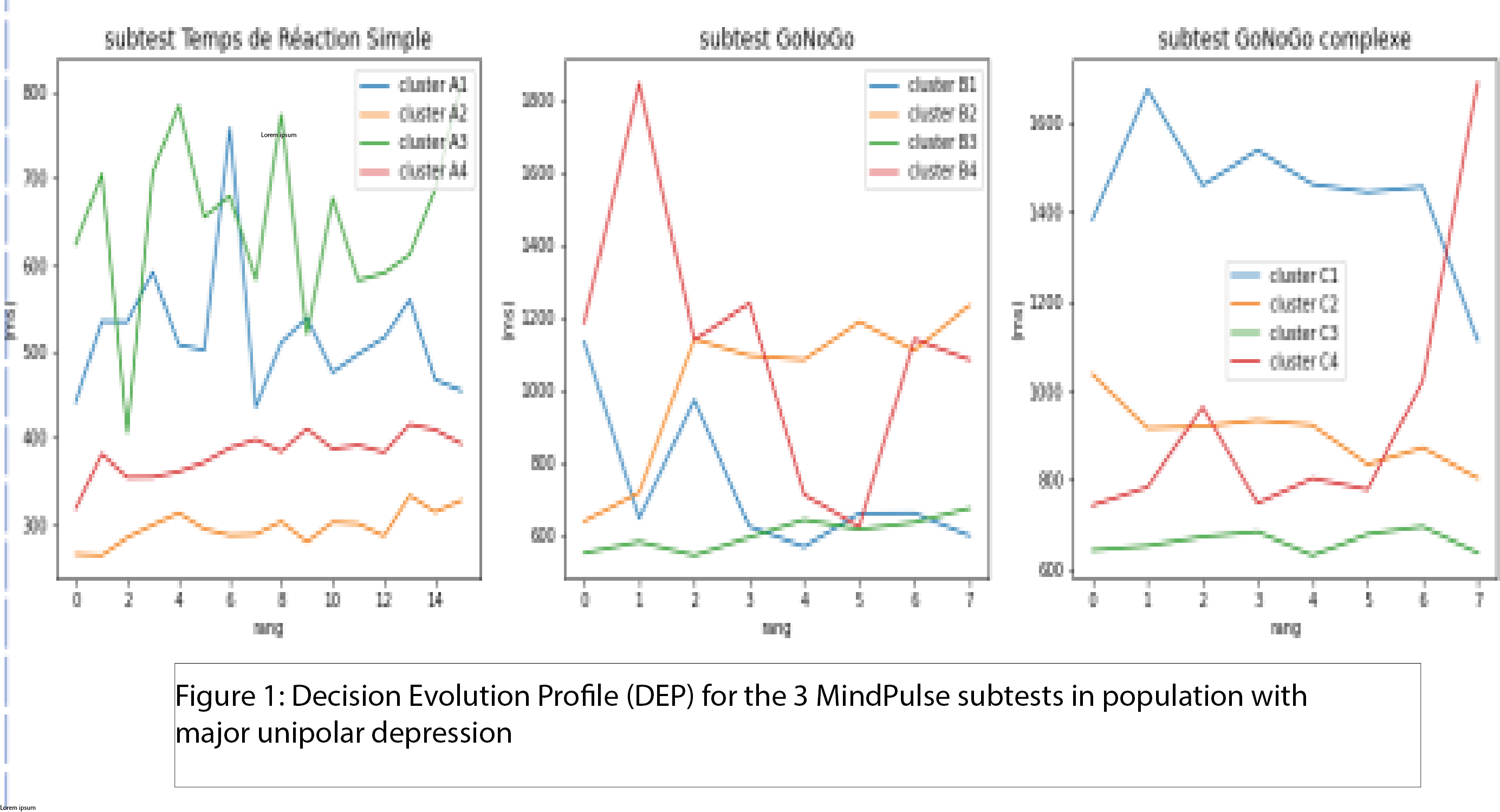
- The profiles generated by AI within our depressed sample shows that only 38% of those participants have a similar strategy than a control sample.
- There is a difference in DEP in depressed patients that can be linked to clinical symptomatology.
Conclusion:
- MindPulse is both correlated to the usual tools used in neuropsychology and the only one having a correlation to clinical observation. MindPulse therefore enable Reliability and Sensibility.
- MindPulse enable to measure both executive and perceptivo-motor slowing in a sample of 46 participants with major unipolar depression.
- Artificial Intelligence gives major information on on decision evolution profiles changes within a population of patients with major unipolar depression.
- Adding new tools like AI enable a more dynamical way to observe adaptation throughout a task and to extract adaptation characteristics with an intensity and difficulty gradient over time.
- Our past static models can now become dynamic.
Those new technologies aim to extract reliable cognitive biomarkers and pathological markers to improve and specify a treatment plan.
